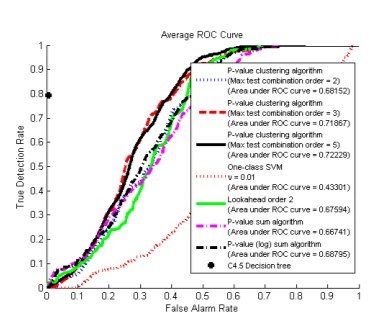
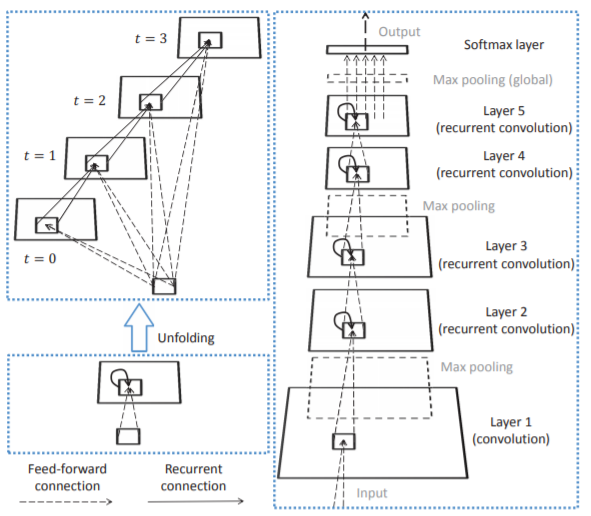
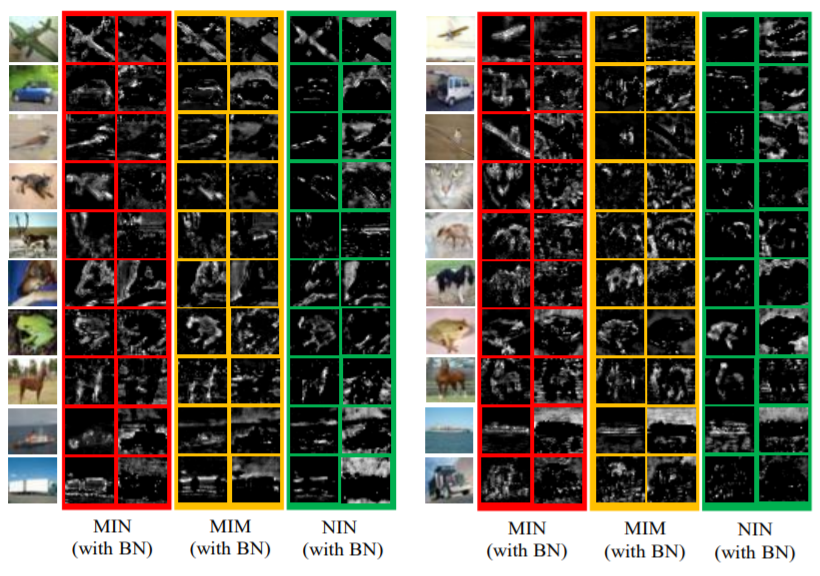
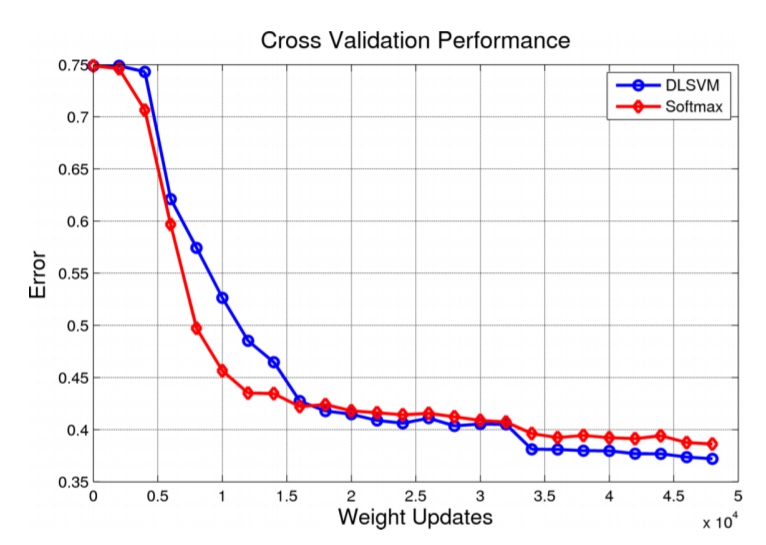
LinkDroid: Reducing Unregulated Aggregation of App Usage Behaviors
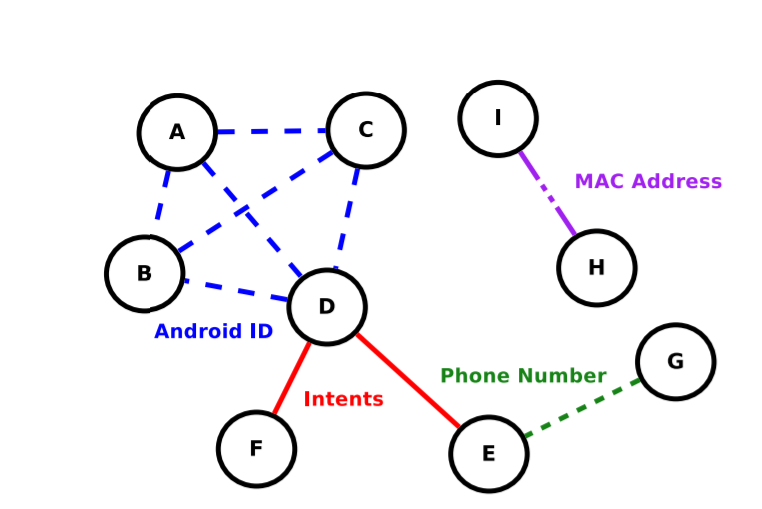
Usage behaviors of different smartphone apps capture different views of an individual’s life, and are largely independent of each other. However, in the current mobile app ecosystem, a curious party can covertly link and aggregate usage behaviors of the same user across different apps. We refer to this as unregulated aggregation of app usage behaviors. […]
LinkDroid: Reducing Unregulated Aggregation of App Usage Behaviors Read More »