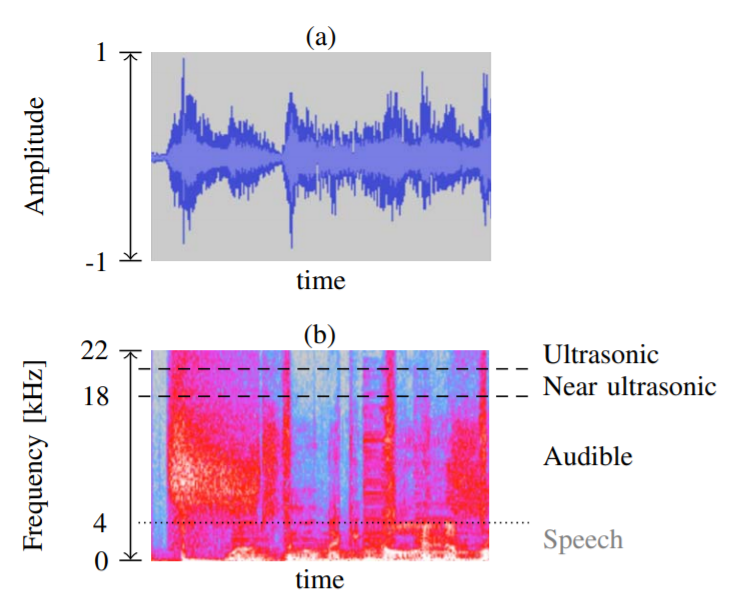
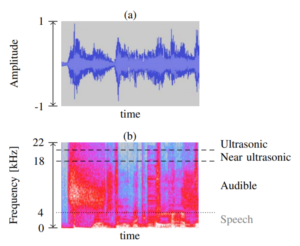
Device tracking is a serious threat to the privacy of users, as it enables spying on their habits and activities. A recent practice embeds ultrasonic beacons in audio and tracks them using the microphone of mobile devices. This side channel allows an adversary to identify a user’s current location, spy on her TV viewing habits or link together her different mobile devices. In this paper, we explore the capabilities, the current prevalence and technical limitations of this new tracking technique based on three commercial tracking solutions. To this end, we develop detection approaches for ultrasonic beacons and Android applications capable of processing these. Our findings confirm our privacy concerns: We spot ultrasonic beacons in various web media content and detect signals in 4 of 35 stores in two European cities that are used for location tracking. While we do not find ultrasonic beacons in TV streams from 7 countries, we spot 234 Android applications that are constantly listening for ultrasonic beacons in the background without the user’s knowledge. The link of the paper: www.sec.cs.tu-bs.de/pubs/2017a-eurosp.pdf